
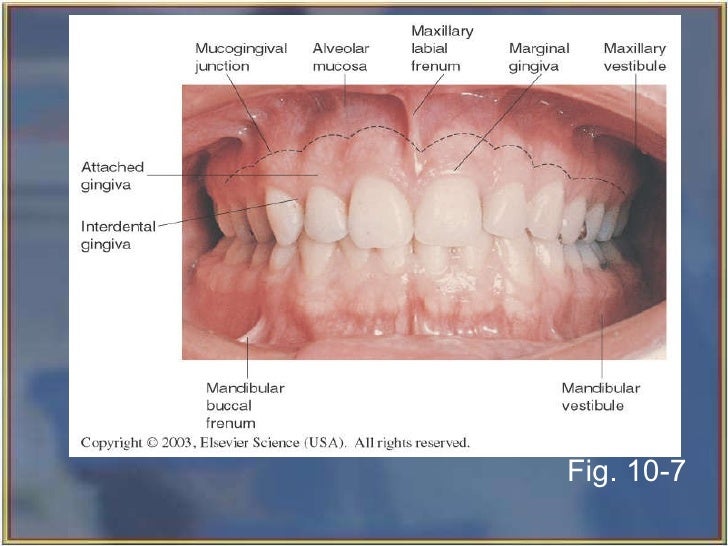
Maxillary Landmarks Labial frenum, Incisive papilla, Buccal frenum, Maxillary alveolar ridge
The easiest anatomical landmark in the floor of the mouth examination, is the curvature of the tongue's surface. Also important is the determination of the air-tissue interface [3, 6]. Intraoral probes are more useful when we want to examine the tongues surface since they are easier to handle in such a small region.

Anatomical Landmarks of Edentulous Jaw. Dental hygiene student, Dental assistant study, Dental
We have created 110 medical original illustrations of the mouth, the buccal cavity, the bones of the palate, the tongue, the salivary glands and the oral part of the pharynx with vessels and nerves.

Anatomical Landmarks of the Mouth AmberaresKing
The stomatognathic system includes various anatomical structures, which allow the mouth to open, swallow, breathe, phonate, suck and perform different facial expressions. These structures are the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), jaw and mandible, muscle tissues and tendons, dental arches, salivary glands, as well as the hyoid bone and the muscles that connect the latter to the scapula and the.

Anatomic Landmarks Dentures Mouth
Figure 2 below, includes many of the normal anatomical landmarks that will be visible on a diagnostic panoramic image. The maxillary sinuses are radiolucent and can be found bilaterally on either side of the nasal septum. The zygomatic process is a vertical, radiopaque line that forms the anterior portion of the zygomatic arch (cheekbone)..

Facial landmarks divided into anatomical and pseudoanatomical... Download Scientific Diagram
Anatomy of the Oral Cavity Joe Iwanaga & R. Shane Tubbs Chapter First Online: 06 November 2021 1225 Accesses 1 Citations Abstract In this section, the surface structures of the oral cavity, which is necessary to understand the mimetic muscles and floor of the mouth, will be reviewed. Download chapter PDF 3.1 Surface Anatomy of the Oral Cavity

Mouth Teeth Diagram with Label coordstudenti
A thorough knowledge of oral anatomy helps the clinician in identifying enough landmarks that in turn act as positive guides in treatment planning. In the present article, a review of all the intraoral anatomical landmarks is been presented and analyzed Keywords: Maxillary ridge, Mandibular ridge, Edentulism, Anatomical landmarks

landmarks found in the oral cavity
Familiarity with the radiologic anatomy and landmarks of the floor of the mouth is helpful for detecting and characterizing pathologic processes that occur there and extend to deep tissues and beyond. A wide range of pathologic processes may involve the floor of the mouth, the part of the oral cavity that is located beneath the tongue.
landmarks of face and oral cavity
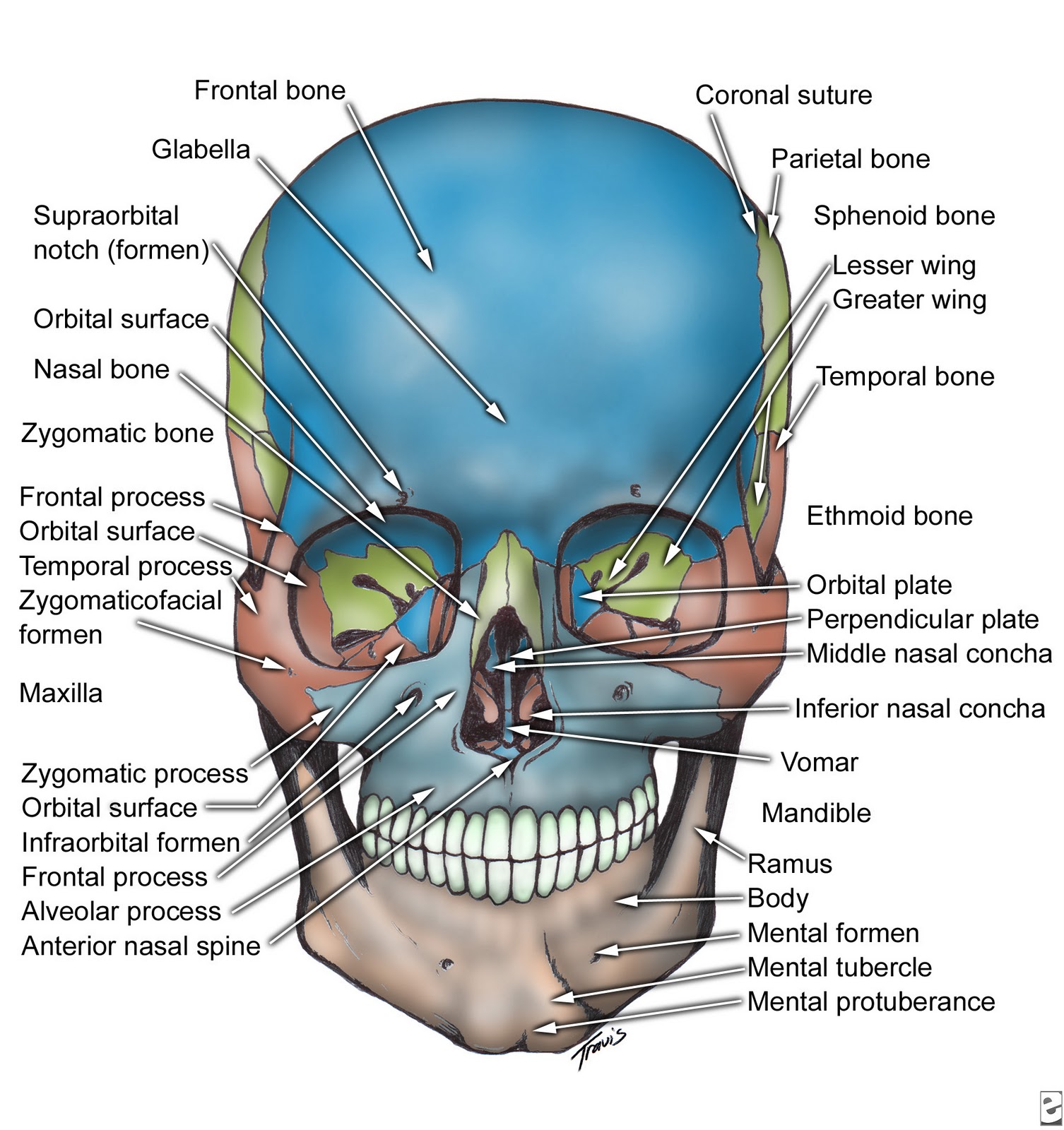
Normal Anatomic Landmarks of the Head Neck and Oral Cavity Bone Structure of the Face Facial Landmarks Landmarks in the Oral Cavity Teeth in the Oral Cavity Types of Teeth, Structures, Location and Functions Divisions and Components of the Teeth Types of Teeth and their Functions Surfaces of the Teeth Dentitions Primary Dentition

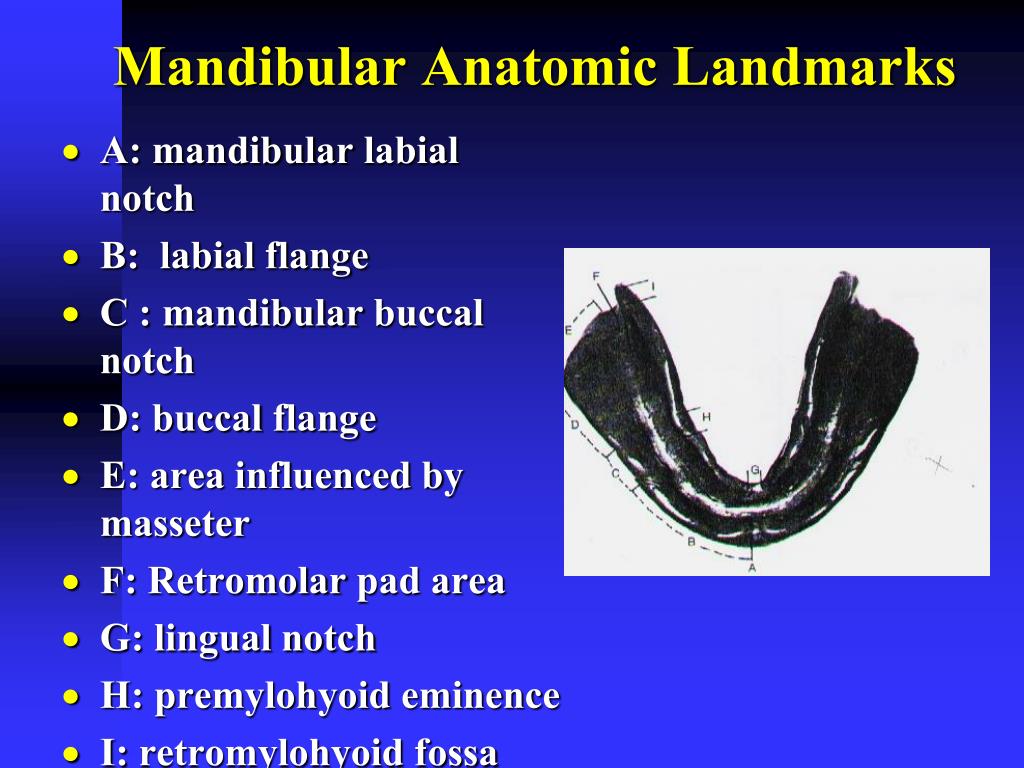
Anatomical landmarks in mandibular edentulous arch YouTube
Landmarks of the oral tissues include the palate, tongue, cheeks and floor of the mouth. It is significant to recognize the normal appearance of these structures during an intraoral examination of the patient. Fauces - Passageway from oral cavity to pharynx.

Oral cavity anatomy with educational labeled structure vector illustration
The maxillary and mandibular edentulous soft tissue anatomy within the denture space of the oral environment is shown in Figure 1. Anatomical landmarks such as the retromolar pads, external oblique, mentalis muscle, frenum attachments, mylohyoid ridge, tuberosities, hamular notches, incisive papilla, labial sulcus, and buccal vestibule are.
Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology CHAPTER 7 Anatomy of Bones and Joints
1. Describe the basic anatomy of the ear, nose, mouth, and throat. 2. Perform a basic examination of the ear, nose, mouth, and throat, identifying normal and pathological conditions. 3. Properly use an otoscope to examine the ear and the nose. 4.
vestibule anatomy mouth
The uvula hangs downwards from the soft palate. The mylohyoid muscles constitute the floor of the oral cavity proper. A mucous membrane known as the oral mucosa is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and forms the inner lining of the mouth.
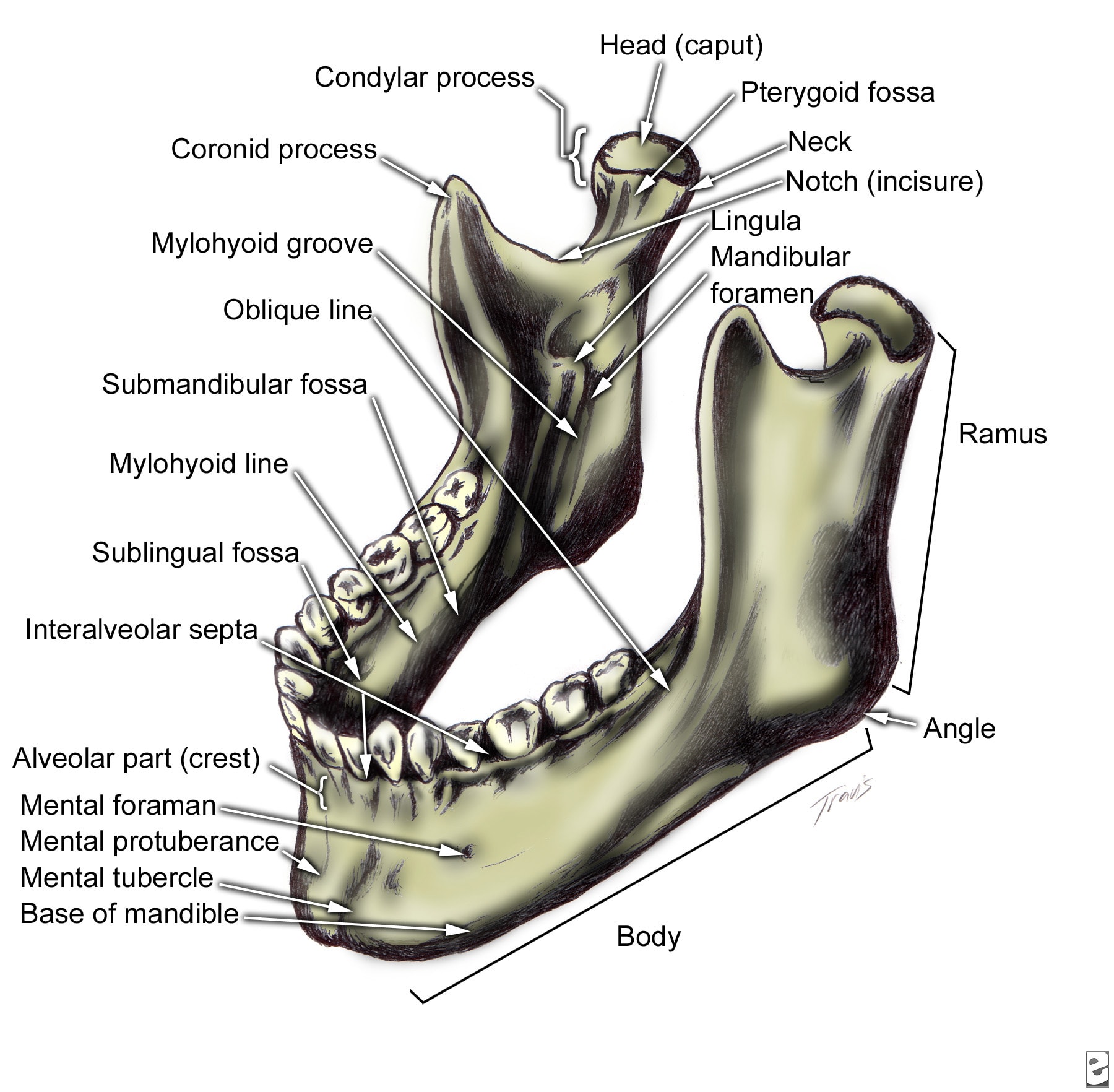
ORAL & MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY Facial Bone Anatomy
The cavity is separated into anterior and posterior parts by the dental arches (or teeth): the anterior oral vestibule sits anteriorly to the teeth and behind the lips, whilst the oral cavity proper describes the area behind the teeth.

Dentistry lectures for MFDS/MJDF/NBDE/ORE Anatomical Landmarks Of Panoramic Radiographs
The tooth is one of the most individual and complex anatomical as well as histological structures in the body. The tissue composition of a tooth is only found within the oral cavity and is limited to the dental structures. Each tooth is paired within the same jaw, while the opposing jaw has teeth that are classified within the same category. However they are not grouped according to structure.

Surrounding Muscles of Upper Complete Denture. Dentistry, Dental hygiene student, Dental
Revisions: 15 format_list_bulleted Contents add The oral cavity, better known as the mouth, is the start of the alimentary canal. It has three major functions: Digestion - receives food, preparing it for digestion in the stomach and small intestine. Communication - modifies the sound produced in the larynx to create a range of sounds.
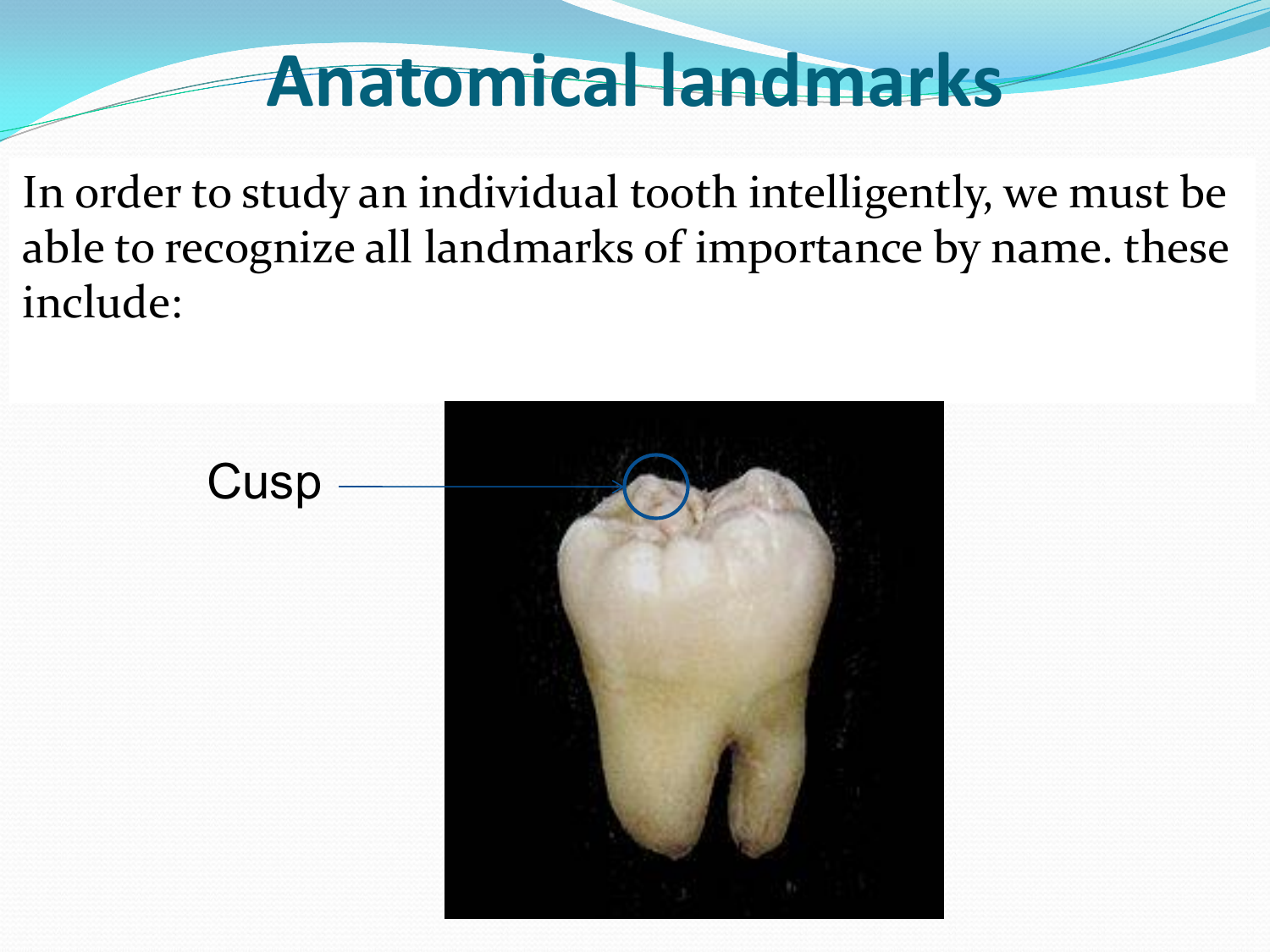
Anatomical landmarks
Hand: Anatomy, is a complex. Diagram of the mouth and lips showing their different components and landmarks. Image: "The mouth includes the lips, tongue, palate, gums, and teeth" by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 4.0 Movement. Numerous muscles are responsible for movement of the lips.